A groundbreaking study has unearthed a remarkable secret to extending healthy lifespans. Taurine, a nutrient found naturally in the body and certain foods, has been shown to hold incredible anti-aging potential. Recent research study lead by Vijay Yadav, assistant professor of genetics and development at Columbia University reveals that Taurine supplementation can significantly slow down the aging process in animals, sparking intrigue and hope for similar effects in humans.

Introduction:
A groundbreaking study published in the Science Journal reveals that taurine, a nutrient naturally produced in the body and found in certain foods, holds remarkable potential for slowing down the aging process. Researchers have discovered that taurine deficiency in animals accelerates aging, while taurine supplementation has been shown to extend the healthy lifespans of mice, monkeys, and worms. These findings have sparked interest in exploring the effects of taurine on human aging.
Illustration Credit: Columbia University Irving Medical Center
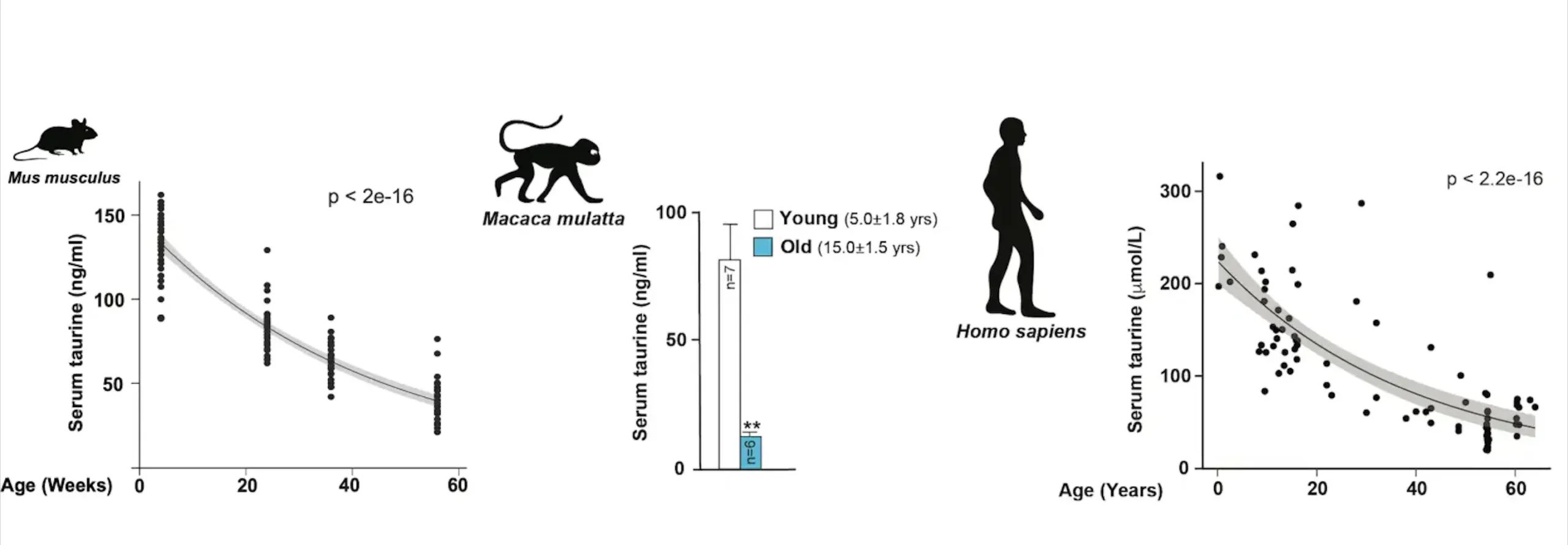
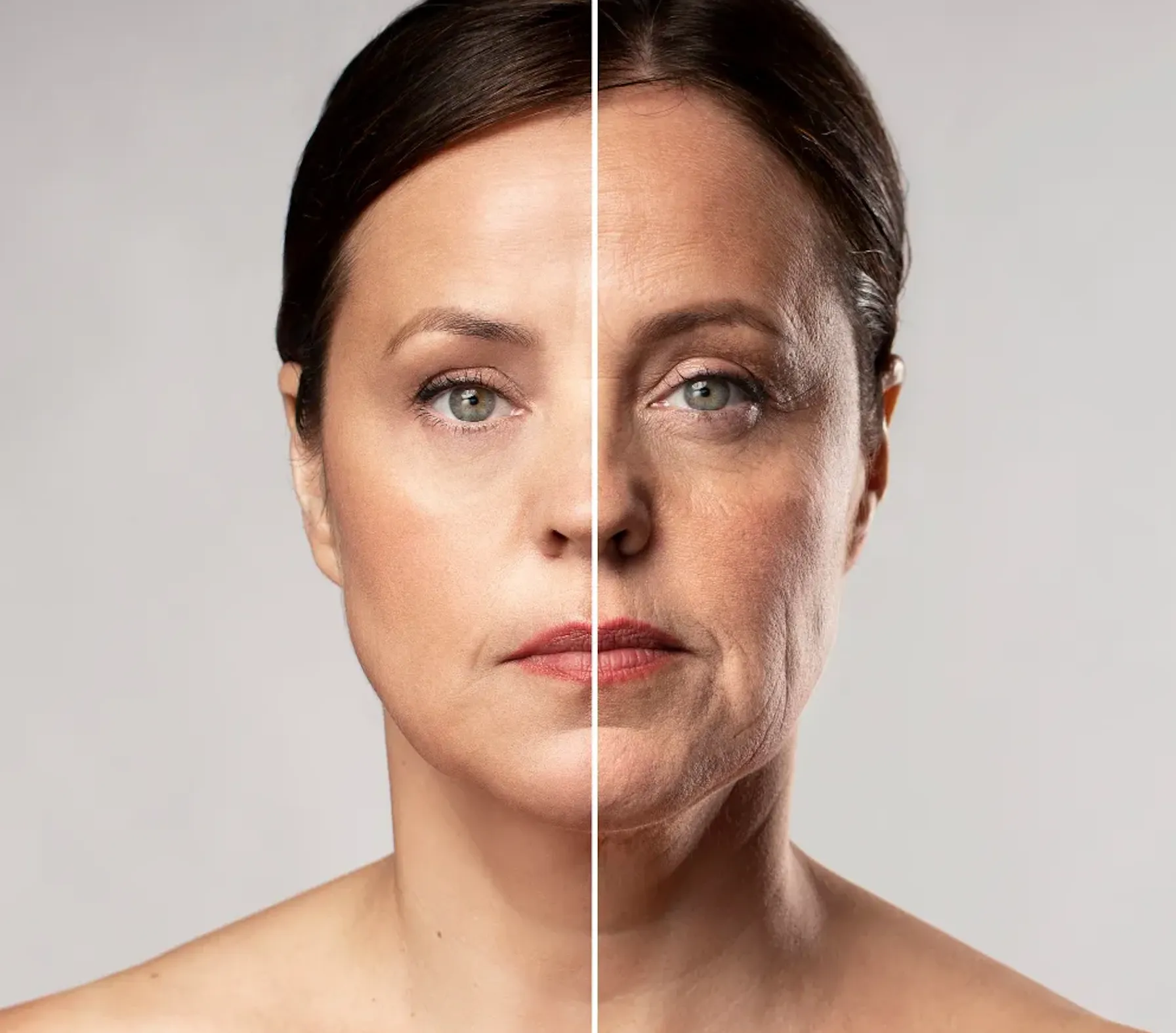
Decline of Taurine with Age: The study highlights that taurine concentrations decline significantly with age in mice, monkeys, and humans.
By analyzing blood samples, researchers found that taurine levels decreased by an estimated 80% throughout the normal human lifespan. This decline led scientists to investigate whether taurine deficiency contributes to the aging process.
Illustration Credit: Columbia University Irving Medical Center
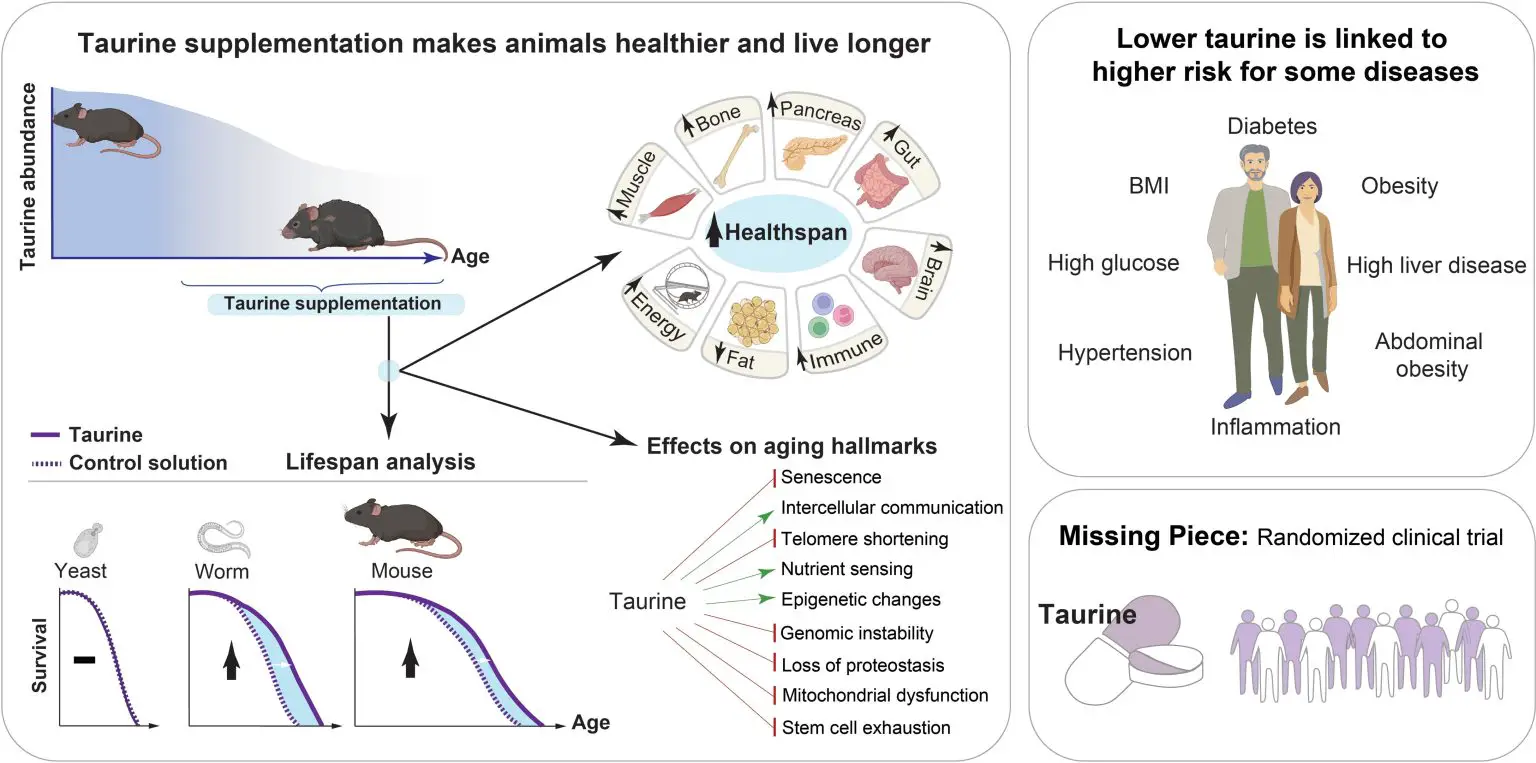
Positive Effects on Animals:
In a series of experiments, researchers tested the effects of taurine supplementation on various animal species. In middle-aged mice, daily oral taurine supplementation resulted in a 10-12% increase in median lifespan, along with an impressive 18-25% increase in life expectancy at 28 months. These mice also exhibited improved bone density, muscle strength, coordination, memory, and overall markers of aging.
Similar outcomes were observed in rhesus monkeys, as a six-month taurine supplementation regimen led to reduced weight gain, improved bone density, and enhanced markers of liver and immune function. Notably, monkeys also showed a decline of approximately 85% in taurine levels between the ages of 5 and 15.
Health Benefits in Humans:
To explore the potential effects of taurine on human aging, the researchers analyzed a sample of 12,000 European adults over the age of 60. According to early findings, taurine concentrations in older people were around 80% lower than in younger ones. Individuals with greater taurine levels also had decreased incidences of type 2 diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and inflammation.
In a separate study involving both athletic and sedentary individuals, it was discovered that taurine levels increased in all participants after exercise. This suggests that exercise may contribute to the health benefits associated with higher taurine levels.
Implications and Caution:
The findings of this study offer a promising avenue for further research into taurine supplementation as a potential anti-aging therapy. While the results indicate a correlation between taurine deficiency and aging-related health issues, it is important to note that causation has yet to be established. Researchers emphasize the need for long-term human randomized control trials to confirm these findings and determine optimal dosage levels for taurine supplementation.
Experts also caution against solely relying on taurine supplementation, as a balanced and nutritious diet rich in plant-based foods is associated with overall human health and longevity. It is crucial to approach taurine supplementation with caution and further investigate potential risks and interactions with other factors.
Conclusion:
The recent study on taurine supplementation has unveiled promising insights into the role of this nutrient in extending healthy lifespans in animals. Taurine deficiency appears to be associated with accelerated aging, while supplementation has demonstrated significant improvements in lifespan and various health parameters.
While further research is needed to establish causality and determine the optimal dosage for humans, these findings open up new possibilities for advancing our understanding of aging and exploring potential interventions for promoting longevity and overall health.
Stay connected with Today On Globe for the latest Global Issues and News Updates.
Explore more related articles at [TOG News / TOG Article]